

R&D Tax Credits
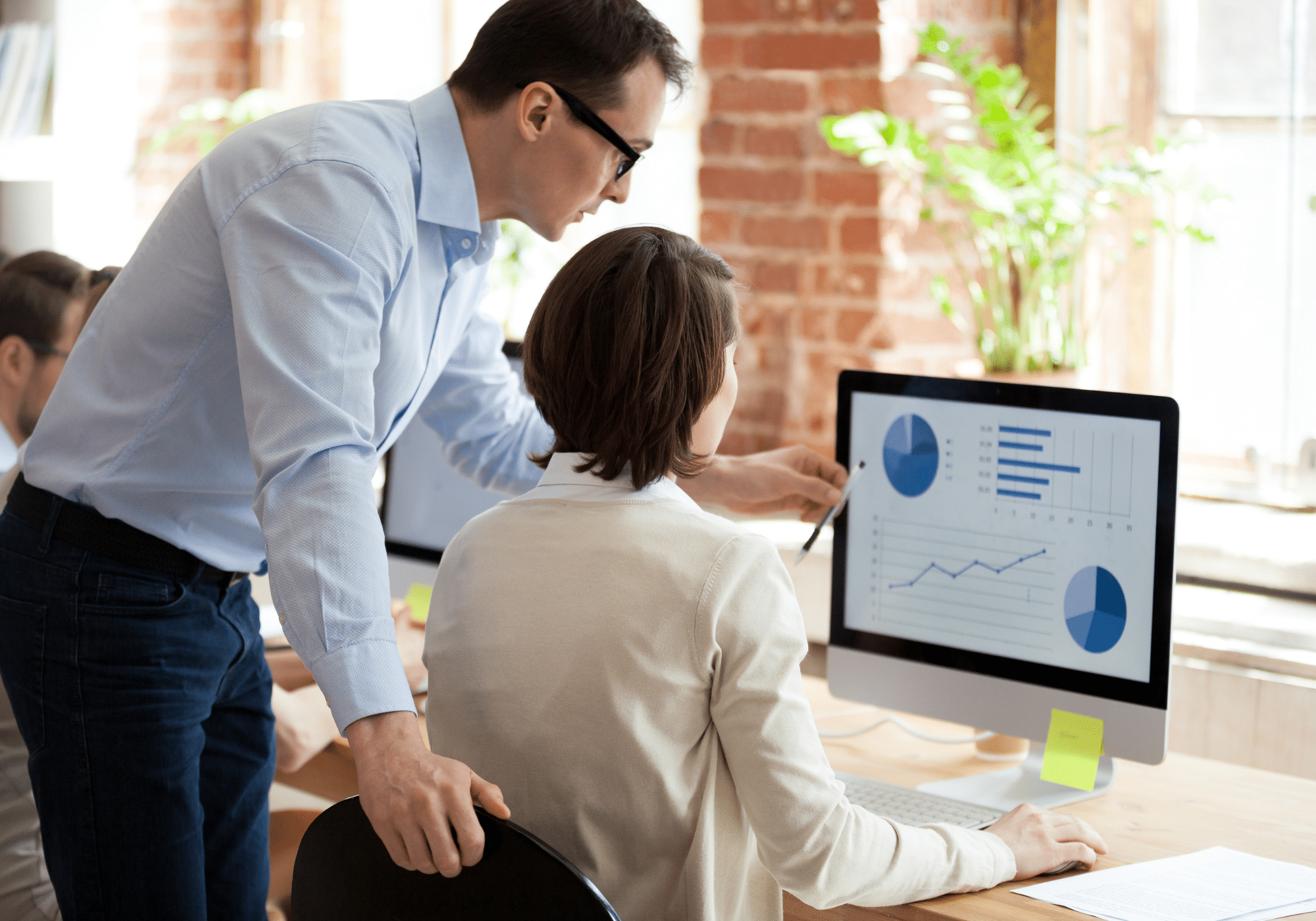
ABGi simplifies the process of claiming R&D tax credits, providing a comprehensive start-to-finish service.


ABGi simplifies the process of claiming R&D tax credits, providing a comprehensive start-to-finish service.
Our expertise in this field has enabled us to secure millions of pounds in benefits for our clients in the UK, with an average of £3.3 million in eligible claims being identified on a weekly basis. We have internal measures in place to reduce your risk of an HMRC enquiry, with our team ready and able to defend any part of your claim if needed.
The UK Government’s Research & Development (R&D) Tax Credit Scheme has been in place since 2000 in order to incentivise businesses to invest in projects focused on innovation.
This scheme has enabled over 89,000 Limited Companies across the country to receive a total of £6.6bn in tax relief during the last year alone. The scheme is open to Limited Companies only, whereas sole traders and partnerships are not included. When claiming R&D Tax Credits, businesses can receive either a reduction in their tax bill or cash credits for loss-making companies.
R&D tax relief can provide a number of significant tax benefits for businesses. These include reducing taxable profits, creating losses where none existed previously, or increasing pre-existing losses.
There have been significant changes to the R&D Tax Relief regime over the last year, impacting accounting periods commencing on or after April 1st, 2023, with additional modifications taking effect from April 1st, 2024.
Summary
Change in the rates of reliefs for the SME R&D scheme from April 2023
Change in the rates of reliefs for RDEC from April 2023
From 1st April 2024 – Introduction of R&D Intensive SME Scheme
From 1st April 2024 – Introduction of merged R&D scheme


From 8th August 2023 – Introduction of the Additional Information Form (AIF) – mandatory compliance form completion
Claim ‘signed off’ by a named officer of the company
Claims must include details of any associated agents
Claims rejected if not completed properly.
Claimaints must submit a pre-notification of their claim, if companies are new claimants or have not claimed in the previous 3 accounting periods
First-time relief-claiming businesses (or businesses who have not claimed in the last three financial periods) must submit a pre-notification of their claim to HMRC online. This gives HMRC the opportunity to take proactive steps in educating companies on valid R&D processes and also provides extra safeguards against reliefs being illegally claimed


From 8th August 2023 – Introduction of the Additional Information Form (AIF) – mandatory compliance form completion
Claim ‘signed off’ by a named officer of the company
Claims must include details of any associated agents
Claims rejected if not completed properly.


Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) are defined as companies with fewer than 500 FTE employees and either total revenues lower than €100 million or total balance sheet assets lower than €86 million. SMEs have access to the Small Business Rate Relief Scheme, which offers tax relief at a rate of up to 230%. Loss-making SMEs can also surrender losses to HMRC for a cash credit.
Large companies are generally defined as companies with 500 or more FTE employees, or those which have fewer than 500 employees but revenue in excess of €100 million and balance sheet assets greater than €86 million. If SMEs meet certain conditions, they may have to claim under the RDEC scheme.

The Research and Development Expenditure Credit (RDEC) scheme was introduced in 2013 and provides Large Companies and SMEs forced to claim under RDEC, a payable cash sum, if they are loss-making or an offset of tax payable if they are profitable. This replaced the Large Company Scheme from 1st April 2016. For expenditure from 1st April 2023, the Research and Development Expenditure Credit (RDEC) rate will increase from 13% to 20%.
There may be a discrepancy between what is considered R&D for the average person and HMRC’s definition. This can result in wasted time or, in the worst-case scenario, an HMRC investigation.
Eligible R&D activities can:
Occur in almost any industry attempting to improve efficiency, speed, size, scale, etc. Even include the replication of a product, process, service, or device if it results in a significant improvement.
According to HMRC, a company is engaged in R&D when they are:
Resolving technological uncertainties that lead to… Advancements in technology that are not easily discoverable by a skilled professional.
Encouragingly, R&D is still considered to have taken place regardless of whether the project was successful or not. The focus is on the “seeking” aspect.

Notifications